
Default values will be entered for unspecified parameters, but all values may be changed. The data will not be forced to be consistent until you click on a quantity to calculate. This calculation is designed to allow you to enter data and then click on the quantity you wish to calculate in the active formula above. This resolvance implies that the wavelength resolution is For a given order and wavelength, the smaller the value of d, the greater the angle of diffraction. If N = slits are illuminated, then the resolvance R =. dsin n The number of slits per metre on the grating, N 1/ d where d is the grating spacing. There is a good case for describing it is the most important invention in the sciences.

The resolvance of such a grating depends upon how many slits are actually covered by the incident light source i.e., if you can cover more slits, you get a higher resolution in the projected spectrum. The diffraction grating was named by Fraunhofer in 1821, but was in use before 1800. The displacement from the centerline for maximum intensity will be Projected on a screen at distance D = cm, The slit separation is d = micrometers = x10^ m.įor incident light wavelength λ = nm at order m = ,
Diffraction grating formula minima how to#
However, angular separation of the maxima is generally much greater because the slit spacing is so small for a diffraction grating.ĭisplacement y = (Order m x Wavelength x Distance D)/( slit separation d)įor a diffraction grating with lines/mm = lines/inch, The Complete Guide to Everything 74K subscribers Subscribe 11K views 2 years ago In this video I will show you how to derive the diffraction grating formula step by step. Units analysis All physical quantities have units.


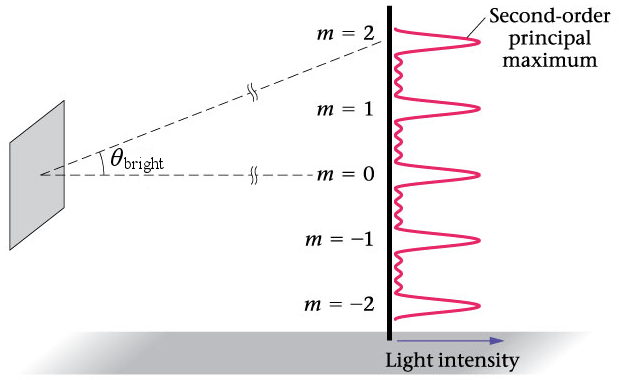
(b) Two point-light sources that are close to one another produce overlapping images because of diffraction. The intensity is proportional to the square of the amplitude, so. 1: (a) Monochromatic light passed through a small circular aperture produces this diffraction pattern. This equation relates the amplitude of the resultant field at any point in the diffraction pattern to the amplitude N E 0 at the central maximum. will estimate width of fringes, then compute intensity distribution on screen. The effect is most noticeable when the aperture is small, but the effect is there for large apertures as well. There are now more minima (dark fringes), because there are more ways to get. Answer: Explanation: The time taken by the object to reach the ground depends up on the vertical velocity of the object. Single slit pattern Circular obstacle Diffraction class of wave phenomena such as spreading and bending of waves passing through an aperture or by an object. The condition for maximum intensity is the same as that for a double slit. Fully-constructive interference fringes thus occur at d sin m, as before. Collimated (parallel) monochromatic light past a narrow slit a pattern of maxima and minima in intensity on a screen. The phasor approach accounts for the downward slope in the diffraction intensity (blue line) so that the peak near m=1 occurs at a value of θ ever so slightly smaller than we have shown here.A diffraction grating is the tool of choice for separating the colors in incident light.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
